If done correctly, trading can be a great way to earn profit. But how do you start? This guide gives you tips and strategies to succeed
Trading can be an effective way to build wealth, but it also comes with significant risks and considerations. To be successful, one must have a deep understanding of the financial markets and a solid strategy for placing trades.
But what if you’re just new to the craft?
In this article, Wealth Professional answers the question, “How do I start trading?” We will give you an overview of how trading works, including the different assets you can trade and trading strategies you can use. We will also provide a step-by-step guide on how to make your first trade.
This guide is part of our client education series and designed for beginners who want to dip their toes into trading. We also encourage financial advisors, who frequently visit our website, to share this with contacts who may be keen on starting their trading career.
How does trading work in Canada?
Trading involves buying and selling different assets with the goal of earning a profit. To achieve this, you will need to speculate whether the price of an asset will rise or fall. In doing so, you have two options:
- You can go long (buy) if you anticipate the market price to rise.
- You can go short (sell) if you expect the market price to drop.
If your speculation is correct, you make a profit. If the market moves against your position, you incur a loss. This is why a deep understanding of the financial market is crucial for you to succeed on this path.
Trading is quite similar to investing: both involve buying and selling assets to maximize returns. The main difference lies in the timeline.
In trading, you use short-term strategies to earn profit, often buying and selling assets multiple times daily, weekly, or monthly. Investing, meanwhile, involves buying and holding onto assets for an extended period to reap larger gains.
If you feel like a long-term approach fits your financial goals better, this guide on how to start investing in Canada can be a useful resource.
What are the different types of assets you can trade?
A big part of learning how to start trading in Canada is familiarizing yourself with the different asset classes. This enables you to take advantage of each asset’s strengths, helping you make informed trading decisions.
If you’re just a beginner, these are the best assets to start your trading career with:
1. Stocks
Also called equities, stocks entitle you to a share of ownership in a company. Stocks are traded as shares. You can buy and sell shares on designated stock exchanges in Canada, including:
- Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX)
- TSX Venture Exchange
- Canadian National Stock Exchange (operating as the Canadian Securities Exchange)
- Cboe Canada (formerly NEO Exchange/Aequitas NEO Exchange)
- Montréal Exchange
You can find the complete list of designated stock exchanges in the country on the Department of Finance’s website.
Traders can make money from stocks in two ways:
- buying stocks at a lower value than when selling them
- dividend capture strategy, which involves buying a stock just before the dividend is paid, holding it just long enough to collect the dividend, then selling it
Trading stocks, however, comes with its own set of risks. A stock’s value can rise or drop, depending on several factors, including:
- the company’s size
- the company’s profitability and financial stability
- the capability of the company’s management team
- general economic conditions
- market competition
- risk exposure
If you sell a stock for more than you purchased it, you will have a capital gain. If you sell for less, you will incur a capital loss.
2. Bonds
Bonds are a type of fixed income securities. When you purchase bonds, you’re essentially lending your money to the government or a private company for a set period. These institutions are then expected to pay a fixed interest rate at certain times and repay the loan amount at the end of the term.
Bonds can often be bought through investment dealers. You can also trade them in the bonds markets of various stock exchanges. As a debt instrument, bond prices are heavily dependent on interest rates.
3. Exchange-traded funds (ETFs)
ETFs are professionally managed portfolios consisting of different asset classes such as bonds and stocks. They work much like mutual funds, pooling money from different investors. This allows you to invest in several products at a lower cost while leaving the investment decisions to a portfolio manager.
ETFs and mutual funds, however, have one key difference. While mutual funds trade once a day after the market closes, ETFs trade throughout the day much like stocks. Because of this, ETF shares are also prone to fluctuations.
If you’re working out whether mutual funds or ETFs are a better investment option, this guide can help.
4. Foreign exchange (Forex)
In forex trading, currencies trade against each other as exchange rate pairs. This involves anticipating and capitalizing on changes in currency values.
Forex trading works with you buying a currency while selling another, hoping that the shift in their relative values earns you a profit. If you feel that the euro will strengthen against the US dollar, for example, you may buy euros and sell dollars, with the intention of selling the euros later at a higher price.
5. Commodities
Commodities are natural resources or agricultural products that are then processed for human use and consumption. They can be classified as:
- hard commodities: resources that are mined or extracted from nature, including precious metals, oil, and natural gas
- soft commodities: which are grown and harvested, such as crops and livestock
Trading commodities works similarly to trading stocks. You decide to buy and sell commodities based on your speculation that their prices will change. If you purchase a commodity and its price rises, you can close the trade and earn a profit. You can trade commodities on different online trading platforms and some designated stock exchanges.
Once you’ve gained more experience and are more comfortable with the process, you can start trading with more complex asset classes, including:
-
Options: These are contracts that allow you to buy or sell an asset at a specified price by a certain date. If market prices are unfavourable, you can let the option expire, mitigating your losses
-
Futures: Futures work just like options but with one key difference. Unlike in options trading, where you can let the contract expire, futures trading requires you to buy or sell an asset by the agreed timeframe
-
Contracts for differences (CFDs): A type of derivatives trade, CFDs allow you to profit from price movements without owning the assets. In CFD trading, you agree to exchange the difference in the price from when you open the contract to when you close it
-
Cryptocurrencies: These are digital assets that are issued and maintained in a decentralized system. You can trade in various crypto exchanges, including Kraken, Gemini, and Coinbase. Cryptocurrencies aren’t regulated and can be very volatile, making them a risky investment
You can learn more about how to invest in cryptocurrency in this guide.
What are the different types of trading strategies?
Before you start trading, you must first understand the different trading strategies you can take, so you can pick the one that best suits your financial goals. These are some of the strategies you can adopt based on the frequency of your trading activities.
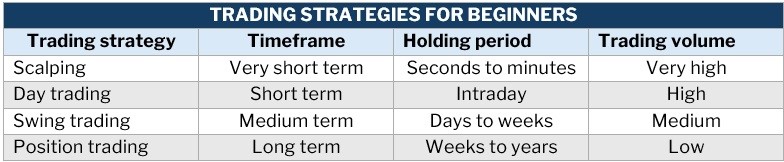
1. Scalping
This strategy suits you if you want to start with very short-term trade with small price movements. With scalping, your goal is to make a small profit from each trade, hoping these little profits accumulate. This strategy, however, requires you to have a disciplined exit strategy as one large loss can wipe off the profit you have built up steadily.
2. Day trading
Also called intraday trading, this strategy is best if you prefer to actively trade during the day, generally as a full-time profession. With day trading, you can take advantage of price fluctuations that happen from when the market opens until the closing hours.
As a day trader, you hold multiple positions open during the day, but careful not to leave them open overnight. This is to prevent exposure to overnight market volatility. In day trading, you will need to have an organized trading plan, so you can quicky adjust to fast movements in the market.
3. Swing trading
In this strategy, you hold a position for a few days or weeks to capture short- to medium-term profits. As a swing trader, you take a technical approach to analyzing the market by studying charts and evaluating price movements to identify trends.
4. Position trading
Here, you hold a position for a long time, usually months or years. Position trading involves ignoring minor price fluctuations in favor of making profits from long-term trends. As a position trader, you use fundamental analysis to assess potential price trends, while factoring in general market trends and historical patterns.
Here’s a summary of the different trading strategies we discussed:
When choosing a trading strategy, it helps to have a good read of the market. Here are some warning signs of an unstable financial market, according to an investment expert.
How to start trading: a step-by-step guide
If you’re just starting your trading journey, the process may seem overwhelming. But with careful planning and preparation, you can carve your way to success. Here’s a 10-step guide on how to start trading for beginners:
Step 1: Learn the basics
Start by building a solid understanding of how trading works. Educate yourself on the basics of the financial market, the different asset classes, and trading styles and strategies. Take time to learn the meaning behind common industry terminologies. This website has an extensive glossary of trading jargon.
Step 2: Choose your market
Different markets have unique characteristics that require different trading strategies. The market you decide to trade in must align with your interests, capital and resources, and risk tolerance.
Step 3: Pick a trading strategy
Each trading strategy requires a different level of industry knowledge and dedication. Choose a strategy that best suits your financial goals.
Step 4: Open a trading account
Selecting where to open a trading account can be overwhelming because of the sheer number of options. Go with a brokerage firm with a solid reputation. It must also provide you with a platform with the tools and resources you need to be successful.
Step 5: Study fundamental and technical analysis
Technical analysis involves price charts, patterns, and indicators. Fundamental analysis, meanwhile, involves economic data and company information. You must be skilled in both to make informed trading decisions.
Step 6: Practice with a demo account
Most brokerage firms offer demo accounts to let you practice trading without risking actual money. These accounts are designed to help you gain valuable experience and test your chosen strategy.
Step 7: Create a trading plan
A sound trading plan gives you direction and helps you achieve your financial goals. It should outline your investment goals, risk management strategy, entry and exit plans, and standards for choosing trading assets.
Step 8: Establish a risk management strategy
Having a risk management plan in place helps protect you against losses. Some common risk mitigation tools and strategies include:
-
Stop-loss order: closes your position automatically if the market moves against you
-
Guaranteed stop: closes your position at the exact price you’ve specified
-
Price alerts: send notifications to help you keep track of market activities
-
Position sizing: helps you determine how many units of assets you can purchase
-
Portfolio diversification: varying the types of assets you trade, knowing that they will perform differently over time
Step 9: Start trading
Begin with small amounts that you can afford to lose. As you gain more experience, you can increase your position size gradually.
Step 10: Don’t stop learning
Trading entails continuous learning. You can keep abreast of the latest trends by checking the news, reading books, and attending webinars and conferences.
You can also learn a lot about the industry by connecting with experts in the trading community – like these winners of our Best Financial Advisors and Professionals Under 40 awards. Find out how these rising stars became among the industry’s most respected and successful leaders in this special report.
Did you find this guide on how to start trading helpful? Let us know in the comments.